Oracle Database
Description
Technical Architecture
The industry’s leading database continues to deliver leading-edge innovations, including machine learning, to enable self-driving data management. This enterprise-proven, database cloud service is designed to support mixed workloads through any deployment strategy, on premises or in the cloud. Experience the power of the next-generation database with unmatched performance, ease, and flexibility.
Oracle Database builds upon the innovations of previous releases such as Multitenant, In-Memory, JSON support, Sharding and many other features that enable Oracle’s Autonomous Database Cloud Services. This latest release of the world’s most popular database also introduces new functionality, providing customers with a multi-model enterprise-class database for all their typical use cases, including:
- Operational database use cases such as; traditional transactions, real-time analytics, JSON document stores and Internet of Things (IoT) applications
- Analytical database use cases such as; traditional and real-time data warehouses and data marts, big data lakes and graph analytics
Oracle Database is the world’s most popular database. Available on cloud and on-premise platforms, Oracle Database 19c is the most recent long term release, with an extended support window. Oracle Database 21c is the latest innovation release, initially available on Oracle cloud through Autonomous Database Free Tier and Database Cloud Service.
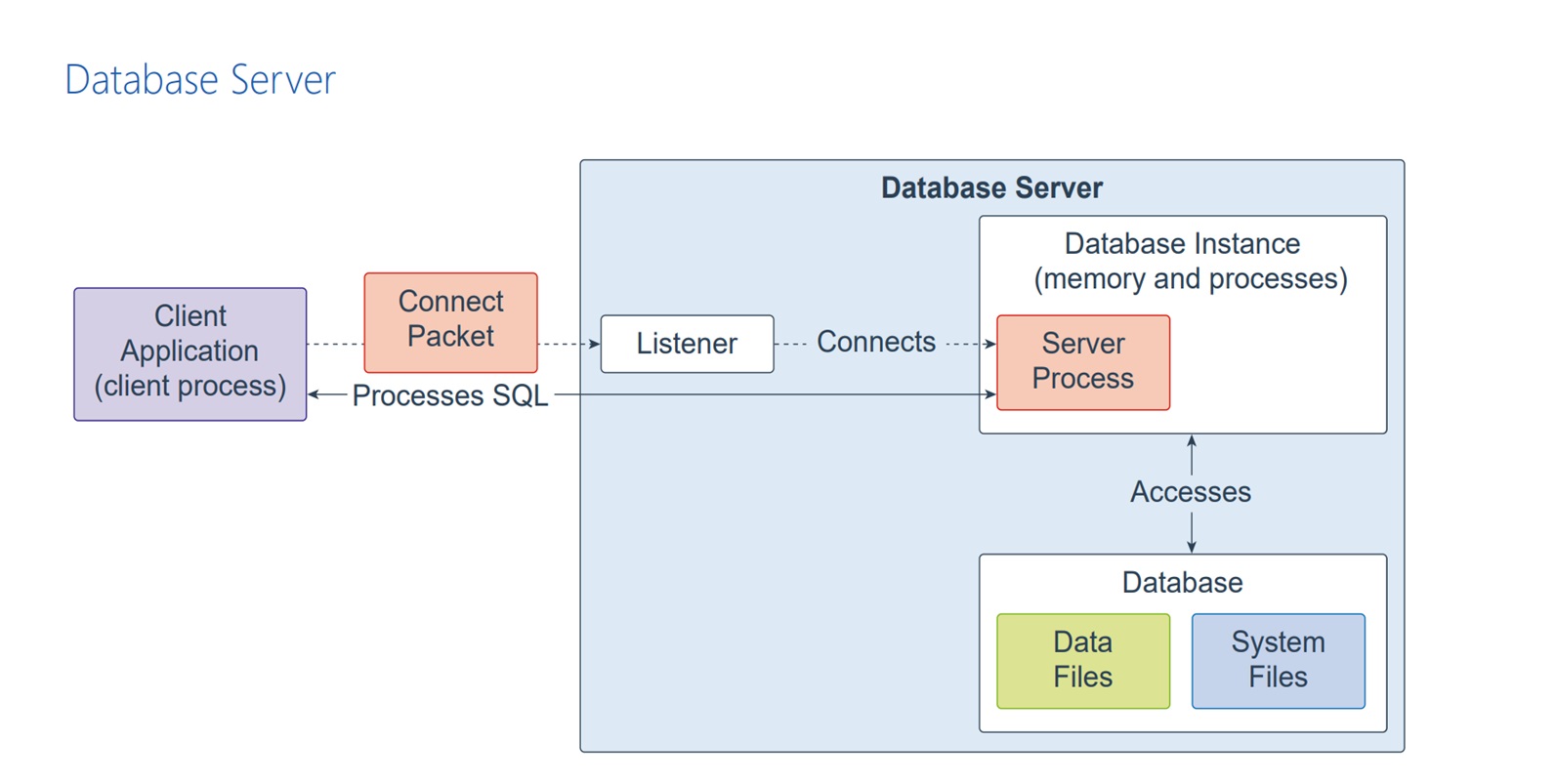
An Oracle Database consists of at least one database instance and one database. The database instance handles memory and processes. The multitenant container database consists of physical files called data files. An Oracle Database also uses several database system files during its operation.
A single-instance database architecture consists of one database instance and one database. A one-to-one relationship exists between the database and the database instance. Multiple single-instance databases can be installed on the same server machine. There are separate database instances for each database. This configuration is useful to run different versions of Oracle Database on the same machine.





